Le protocole CAN bus est un protocole de communication série qui peut utiliser des fils à paires torsadées pour transmettre des signaux, ce qui est plus stable et plus fiable. L'émergence du bus CAN résout le problème de la complexité du câblage et réduit l'utilisation de fils de cuivre pour diminuer le coût, ce qui constitue un avantage certain par rapport aux méthodes conventionnelles de câblage point à point.
CAN2.0A : Format standard utilisant des identificateurs de 11 bits.
CAN2.0B : format étendu pour les identificateurs de 29 bits.
CAN FD : également connu sous le nom de CAN à débit variable, il est compatible avec le CAN2.0 existant, de sorte que les nouveaux dispositifs CAN FD et les dispositifs CAN existants peuvent coexister dans le même réseau de contrôle.
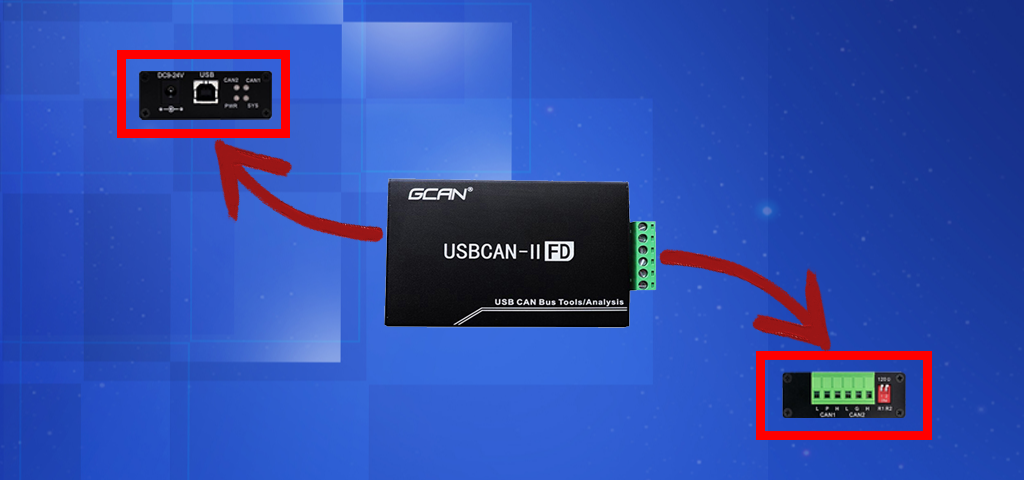
Le protocole de bus CAN est un bus série standard à hôtes multiples permettant de connecter des unités de contrôle électronique (ECU). Les calculateurs sont également appelés nœuds, et au moins deux nœuds doivent être présents sur le réseau CAN pour pouvoir communiquer. Un nœud peut être aussi complexe qu'un simple dispositif d'entrée/sortie ou un composant intégré qui contient un interprète CAN et est équipé d'un logiciel. Un nœud peut également être une passerelle qui permet à un ordinateur ordinaire de communiquer avec des dispositifs sur le réseau CAN via un port USB ou Ethernet.
Tous les nœuds sont reliés entre eux par deux bus parallèles, les deux fils formant une paire torsadée et étant connectés à une impédance caractéristique de 120Ω.
Chaque nœud a besoin de
1. un processeur central, un microprocesseur ou un processeur principal :
Traite les informations de données que l'hôte décide de recevoir et les informations qu'il souhaite transmettre.
Des capteurs, des actionneurs et des dispositifs de contrôle peuvent être connectés au processeur principal.
2. Contrôleur CAN ; fait généralement partie d'un microcontrôleur intégré.
Réception : Le contrôleur CAN stocke les octets sériels reçus du bus, et le processeur principal peut accéder à ce message lorsque le message de données est terminé (généralement grâce au déclenchement d'une interruption par le contrôleur CAN).
Transmission : le processeur principal envoie des informations de transmission au contrôleur CAN, après réception, lorsque le bus est inactif, pour transmettre les informations de bits série au bus.
3, émetteur-récepteur ; défini par la norme ISO11898-2/3 relative aux unités d'accès au support (MAU)
Recevoir : Convertit le flux de données de la couche de bus CAN en une norme utilisable par le contrôleur CAN. Les contrôleurs CAN sont généralement équipés de circuits de protection.
Transmettre : Convertit le flux de données du contrôleur CAN vers la couche du bus CAN.
Chaque nœud peut envoyer et recevoir des messages, mais pas simultanément. Un message ou une trame se compose principalement d'un identificateur (ID), qui indique la priorité du message, et d'un maximum de huit octets de données. Le CAN FD amélioré étend chaque trame à un maximum de 64 octets. Les messages sont transmis en série sur la ligne principale au format NRZ (non-return-to-zero) et peuvent être reçus par tous les nœuds.
Les dispositifs connectés par un réseau CAN sont généralement des capteurs, des actionneurs et d'autres dispositifs de contrôle. Ces dispositifs sont connectés au bus par un processeur central, un contrôleur CAN et un récepteur CAN.
Nous disposons d'une équipe professionnelle de recherche et de développement de bus CAN, avec plus de 20 ans d'expérience indépendante en matière de recherche et de développement, l'entreprise s'occupe des principaux produits suivants Analyseur de bus CAN, Passerelle bus CAN, Contrôleur PLC Si vous avez besoin de produits pour le bus CAN, n'hésitez pas à nous contacter à tout moment !


